Selective Search for Object Recognition using R-CNN
In this article we will learn how to use R-CNN for Selective Search for Object Recognition. Selective Search is an algorithm wused in conjunction with Region-based Convolutional Neutral Networks(R-CNN) for object detection. It addresses a key challenge in object detection: efficiently proposing candidate object location. R-CNN algorithms aim to detect objects within an image by proposing regions likely to contain the objects, which are then analyzed further.
Selective Search will give a large set of possible object locations, which can then be used as input to R-CNN models. It works by hierarchically grouping pixels based on color, texture, size, and shape similarities. These groupings form potential object regions ,which are then merged using a greedy algorithm.
Here’s the code for it:
import cv2
import selectivesearch
import matpolib.pyplot as plt
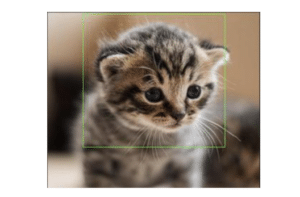
image_path = 'img_2.jpg'
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
bounding_boxes = [(100, 50, 200, 150),(300, 200, 150, 100)]
for (x, y, w, h) in bounding_boxes:
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2_imshow(image)
cv2.waitkey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()output:
The key steps involved in Selective Search are, Initial Region Generation: generate initial regions by grouping pixels based on color, texture, and other features, Region Merging: Merge similar regions iteratively to form larger candidate regions, Object Proposal Generation: Output a set of proposed regions likely to contain objects, which are then passed to an R-CNN model for further analysis.
Selective Search significantly reduces the computational cost of exhaustive region proposal methods, making it efficient for use in object recognition tasks. It integrates with R-CNN using two methods .They are feature extraction and classification. Reduced Computational Cost, Lower Precision, Faster R-CNN etc are some of the advatanges of Selective Search.
Selective Search played a crucial role in the early development of R-CNN for object detection.
Leave a Reply