Morris Inorder Tree Traversal in C++
In this tutorial, we will learn Morris inorder tree traversal in C++. For learning morris inorder tree traversal first we should know about what is inorder tree traversal.
Inorder Tree Traversal:
It is a type of tree traversal in which first we visit Left subtree then Root and then Right Subtree of the graph.

Steps of Morris Inorder Tree Traversal algorithm:
1. Initialize curr as root.
2. If curr->left == NULL {
print curr->data
curr = curr->right
}
else{
Find the inorder predecessor of curr
if predecessor->right==NULL {
predecessor->right=curr
curr=curr->left
}
else{
predecessor->right=NULL;
print curr->data
curr=curr->right
}
}
3. Repeat step 2 until the root becomes NULL.
Flow of Morris Inorder Tree Traversal
Input tree:

Iteration 1:
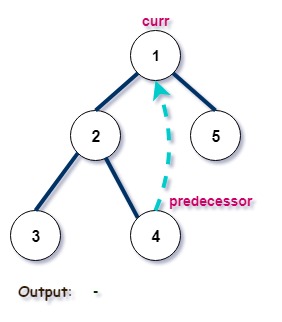
Iteration 2:
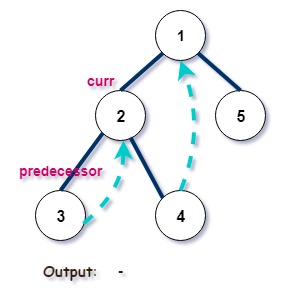
Iteration 3:
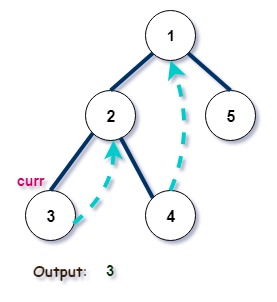
Iteration 4:
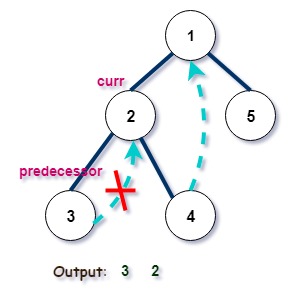
Iteration 5:
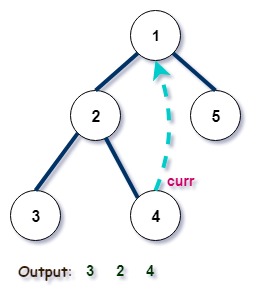
Iteration 6:

Iteration 7:

Program to implement Morris Inorder Tree Traversal in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/* Each node of a tree contains 1 data field and 2 links, 1 link to left child and 1 link to right child */
/* Typedef function is used to assign an alternative name to the existing datatype. Here, using typedef function we can write 'struct Node' as 'Node' */
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
}Node;
Node* new_node(int );
void morris_inorder_traversal(Node*);
Node* find_inorder_predecessor(Node*);
int main()
{
Node* root = new_node(1);
root->left = new_node(2);
root->right = new_node(5);
root->left->left = new_node(3);
root->left->right = new_node(4);
/* this input tree is shown in above figure */
cout<<"\nMorris Inorder Traversal of the graph: ";
morris_inorder_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
/* This function is used to create new node with the given data */
Node* new_node(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
Node* find_inorder_predecessor(Node* curr)
{
Node* predecessor=curr->left;
while (predecessor->right != NULL && predecessor->right != curr)
predecessor=predecessor->right;
return predecessor;
}
void morris_inorder_traversal(Node* root)
{
Node *curr;
curr = root;
while (curr!=NULL)
{
/* if curr doesn't have left child */
if (curr->left==NULL)
{
cout<<curr->data<<" ";
curr=curr->right;
}
else
{
/* finding inorder predecessor */
Node* predecessor=find_inorder_predecessor(curr);
/* Make curr as the right child of its inorder predecessor */
if(predecessor->right==NULL)
{
predecessor->right=curr;
curr=curr->left;
}
else
{
predecessor->right=NULL;
cout<<curr->data<<" ";
curr=curr->right;
}
}
}
}
Output:
Morris Inorder Traversal of the graph: 3 2 4 1 5
Time Complexity & Space Complexity
The Time Complexity and Space Complexity of the program is O(n) and O(1) respectively.
You may also read:
Leave a Reply