Get the current scroll position of a SwiftUI ScrollView
In this tutorial, we will see how to get the current scroll position of a SwiftUI ScrollView.
We can use the ScrollView to create a scroll view and the onChange modifier within the GeometryReader to detect and track the scroll position changes within the ScrollView.
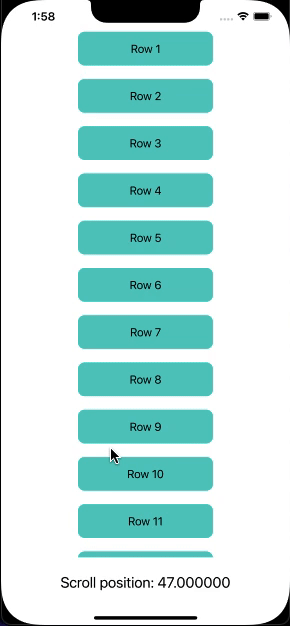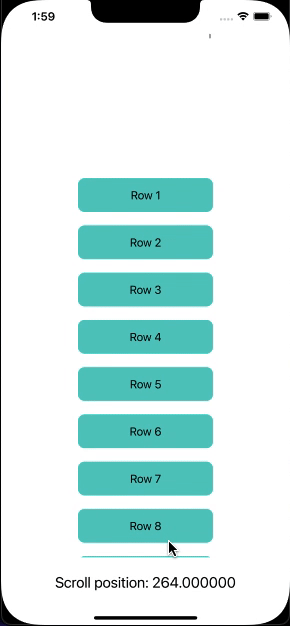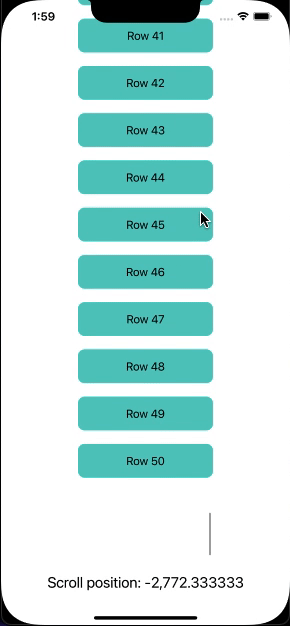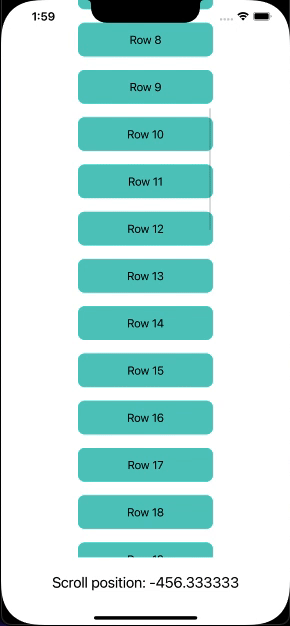
Now, I will create a ScrollView with 50 rows that will be aligned vertically. Then, I will track the scroll position and display the position as a text label at the bottom of the view.
Follow the steps below to achieve this task.
Create a @State variable
First of all, I will create a @State variable to track the vertical scroll position.
Example
@State private var scrollOffset = 0.0
In the above code, I have created a @State variable scrollOffset that will track the vertical scroll position within the view’s content.
Create a ScrollView
Now, I will create a scroll view using the ScrollView with 50 rows. I will use VStack within the ScrollView to align the rows vertically.
Example
ScrollView {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
ForEach(1...50, id: \.self) { index in
// For loop creating rows dynamically from 1 to 50
Text("Row \(index)")
.frame(width: 200, height: 50) // To set width and height for each row
.background(.mint) // To set a mint background color for the row
.cornerRadius(10) //To Round the corners of the row
}
}
}
In the above code, I have used the ForEach loop to create 50 Text views labeled from “Row 1” to “Row 50“.
Then, I have modified every Text view with the frame(), background() and cornerRadious() modifier to make the rows more attractive.
Tracking scroll offset using GeometryReader
Now, I will create a background of the VStack within the ScrollView using the GeometryReader within the background() modifier.
So, we can read the information about the geometry (size and position) of the GeometryReader container.
Example
.background (
GeometryReader { geometry in
Color.clear //To make the GeometryReader (background) invisible
.onAppear {
// Get the initial scroll offset
scrollOffset = geometry.frame(in: .global).minY
}
.onChange(of: geometry.frame(in: .global).minY) { value in
// Update the scroll offset when it changes
scrollOffset = value
}
}
)
In the above code, I have used the .onAppear to get the initial scroll offset, it will capture the initial scroll position of the content and assign it to the scrollOffset variable.
Then, the .onChange to get the scroll offset when we scroll the view. It will update the scrollOffset variable with the new value, whenever we scroll the content.
Here is the complete code below.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var scrollOffset = 0.0
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
ForEach(1...50, id: \.self) { index in
Text("Row \(index)")
.frame(width: 200, height: 50)
.background(.mint)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
.background (
GeometryReader { geometry in
Color.clear //To make the GeometryReader (background) invisible
.onAppear {
// Get the initial scroll offset
scrollOffset = geometry.frame(in: .global).minY
}
.onChange(of: geometry.frame(in: .global).minY) { value in
// Update the scroll offset when it changes
scrollOffset = value
}
}
)
}
// To display the current scroll position
Text("Scroll position: \(scrollOffset)")
.padding()
.font(.title2)
}
}
Output:
Leave a Reply