Dictionary to Pandas DataFrame in Python
When one studies creating Python Dataframes, Creating a Pandas DataFrame from a dictionary is one of the very common ways.
In this tutorial, I’ll guide you through the process step by step. Before we start, make sure you have Pandas installed on your system. If not, you can install Pandas using the following command: pip install pandas.
Code Implementation of Dictionary to DataFrame in Pandas
The first step is to import the Pandas library into your code as everything starts off by importing the necessary modules.
import pandas as pd
Creating a Dictionary (Dataset)
Next, you need a dictionary with key-value pairs that you want to convert into a data frame. For this tutorial, I will make use of a creative concept which is the dataset of a ZOO. We will make use of certain columns namely: ‘Animal Name’, ‘Scientific Name’ and ‘Favorite Food’.
For the Scientific Names obviously, you might require some help from the Internet. Let’s create a dictionary for the same:
ZOO_Database = {
'Animal': ['Lion', 'Giraffe', 'Penguin', 'Elephant', 'Kangaroo'],
'Scientific_Name': ['Panthera leo', 'Giraffa camelopardalis', 'Aptenodytes forsteri', 'Loxodonta africana', 'Macropus'],
'Favorite_Food': ['Zebra', 'Acacia leaves', 'Fish', 'Fruits', 'Eucalyptus leaves']
}Converting to DataFrame
There are multiple ways to convert a dictionary to a DataFrame in Pandas. We will explore one method after another. First of all let’s list all the functions before explaining them in detail:
- pandas.DataFrame()
- pandas.DataFrame.from_dict()
- pandas.DataFrame.from_records()
Using pandas.DataFrame()
This command converts a Python dictionary into a tabular structure with rows and columns, where each column corresponds to a keys in the dictionary, and each row corresponds to an values in the lists associated with those keys.
pd.DataFrame(ZOO_Database)
When we execute the code, we get the following output on the screen:
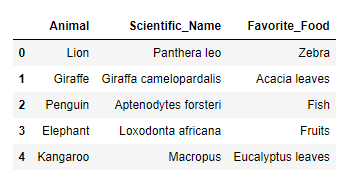
Using pd.DataFrame.from_dict()
This method does the same thing as pd.DataFrame(). It’s just an alternative method that gives you more flexibility in understanding the purpose of the function better as it is specific to dictionaries.
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(ZOO_Database)
When we execute the code, we get the following output on the screen:
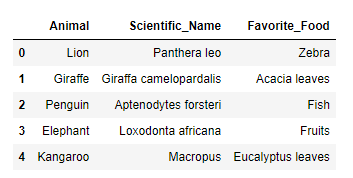
Using pd.DataFrame.from_records()
There might be cases when we have a bunch of dictionaries or let’s say dictionaries nested inside a list where each nested dictionary represents each row. Let’s manipulate the dataset in a way to use the data in the function accurately.
ZOO_Database = [
{'Animal': 'Lion', 'Scientific_Name': 'Panthera leo','Favorite_Food': 'Zebra'},
{'Animal': 'Giraffe', 'Scientific_Name': 'Giraffa camelopardalis','Favorite_Food': 'Acacia leaves'},
{'Animal': 'Penguin', 'Scientific_Name': 'Aptenodytes forsteri', 'Favorite_Food': 'Fish'},
{'Animal': 'Elephant', 'Scientific_Name': 'Loxodonta africana', 'Favorite_Food': 'Fruits'},
{'Animal': 'Kangaroo', 'Scientific_Name': 'Macropus','Favorite_Food': 'Eucalyptus leaves'}
]See how we have aligned the dataset and now the dataset is all ready to be passed for the from_records function. Have a look at the code and output below:
pd.DataFrame.from_records(ZOO_Database)
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully created a Pandas DataFrame from a dictionary and that too with the help of various methods. Hope you liked the tutorial and had a fun time learning something new and interesting.
Also Read:
- Dataframe.get() in Pandas with examples
- Print Pandas DataFrames without Index in Python
- Select rows from Pandas Dataframe Based On Column Values
Happy Coding!

Leave a Reply