Create a digital clock in Python using Tkinter
In this tutorial, we will learn how to create a digital clock in Python using Tkinter. We will be creating digital clock which displays the time on the digital clock. For Creating a digital clock in Python using Tkinter we will be following five steps.
The five steps for creating a Digital Clock in Python using Tkinter are as follows:
1. Importing Modules:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter.ttk import * from time import strftime
We start by importing the necessary modules:
For digital clock in Python we have to import two necessary modules are tkinter and time.
tkinter: This module provides the basic functionality for creating a graphical user interface(GUIs).
time : We use this module to get the current time.
2. Creating the Main Window:
We can create the main application window using tk.Tk( ).
The title of the window is set to “Digital Clock” using root.title(‘Digital Clock’)
3. Defining the Time Function:
We define a function called time( ) that updates the time display every second.
Inside this function:
We use strftime('%H,%M,%S,%p') to format the current time as hours, minutes, seconds, and AM/PM.
The formatted time string is then displayed on a label widget ( lbl ) using lbl.config(text=string).
We schedule the time( ) function to run again after 1000 milliseconds (1 second) using lbl.after(1000, time).
4. Creating the Label Widget:
We create a label widget ( lbl ) to display the time.
The font, background color, and foreground color are set using Label(root, font=(‘calibri’, 40, ‘bold’), background=’purple’, foreground=’white’).
The label can be centered in the window using lbl.pack(anchor=’center’).
5. Running the Application:
We start the Tkinter event loop using root.mainloop( ).
This keeps the application running until the user closes the window.
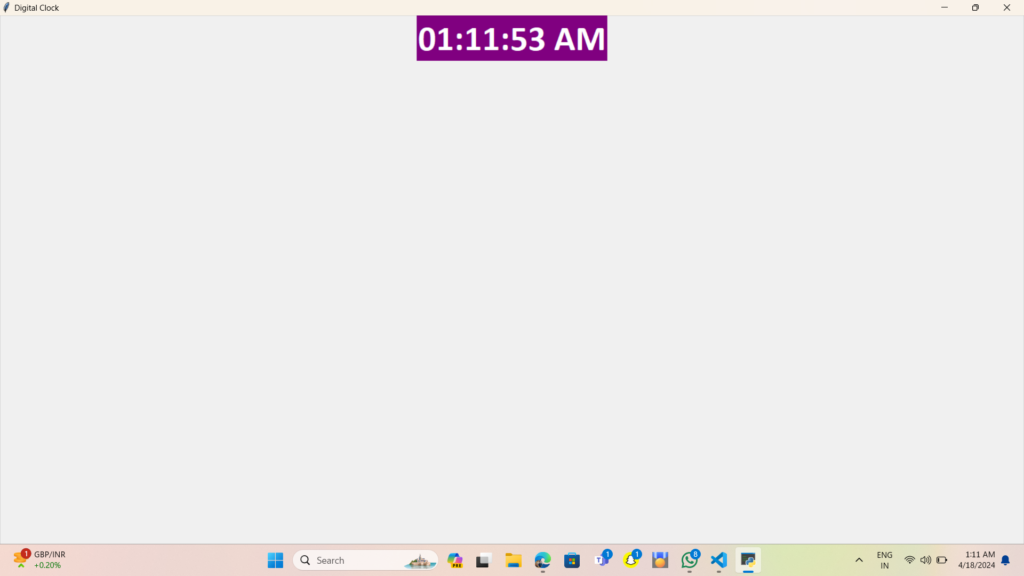
The result is a simple digital clock that updates in real-time! You can run this code on your local machine to see the clock in action.
The above five steps are used to create a Digital Clock in Python using Tkinter.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter.ttk import *
from time import strftime
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('Digital Clock')
def time():
string = strftime('%H:%M:%S %p')
lbl.config(text=string)
lbl.after(1000, time)
lbl = Label(root, font=('calibri', 40, 'bold'), background='purple', foreground='white')
lbl.pack(anchor='center')
time()
root.mainloop()
output:
Leave a Reply