One Hot Encoding of datasets in Python
In this tutorial, we will be learning the process of One hot encoding of datasets. One hot encoding transforms our categorical labels into vectors of zeros and ones. However, our regular machine learning algorithms usually cannot work categorical values and hence these should be converted into numbers. I have considered a fake data set consisting of two columns ‘Gender’ and ‘Nationality’.
One Hot Encoding
I have put up the image of our sample data set:

To use One Hot encoder all of our data must be in numerical form. String values are not accepted by OneHotEncoder. Hence we Label Encode the data first. The modules required are mentioned in the code below.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
df=pd.read_csv('national.csv')label=LabelEncoder() df['Nationality1']= label.fit_transform(df['Nationality']) ohc = OneHotEncoder() #created an instance of OneHotEncoder
After LabelEncoding our DataFrame looks like :
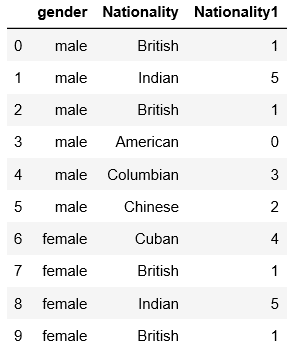
After Label Encoding, we have to fit and transform the column to convert it into the One Hot Encoded form. However, before that, we will have to do some preprocessing of the data.
df2=df['Nationality1'] #separating the column to be df2=df2.to_numpy() #converting Panda series to numpy array df2=df2.reshape(-1,1) #converting 1D array to 2D array df1 = ohc.fit_transform(df2).toarray()
It is a must to have your data in 2-Dimensional form in order to fit and transform it into One Hot Encoded Form. Our One Hot encoded data looks like this:

We finally convert this numpy array into a DataFrame in order to concatenate it to the original dataframe.
df3=pd.DataFrame(data=df1,index=df.index,columns=['American','British','Chinese','Columbian','Cuban','Indian']) #creating a new dataframe consisting of One Hot Encoded data df=df.join(df3,how='right') #joining to the original dataframe from the right side
Our final DataFrame after OneHotEncoding looks like this:

Leave a Reply