Get the current date in every possible format in LaTeX
In this tutorial, You will learn how to get current date in LaTeX and get every possible format of the current date.
In order to get the current date in Month Day, Year format, you can use the \today command.
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
\textbf{Current date is:} \today.
\end{document}Output:

Using datetime package
With the datetime package you can also use the \today command. In this case, you will get the current date in Day-name Day Month, Year format. Take a look.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{datetime}
\begin{document}
\textbf{Current date is:} \today.
\end{document}Output:
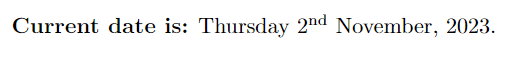
Numerical date format in LaTeX
In order to get a numerical date format of the current date, you can use \ddmmyyyydate with the \today command. Like this \ddmmyyyydate{\today}. Don’t forget to load the datetime package. The date format will be day/month/year.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{datetime}
\begin{document}
\textbf{Current date is:} \ddmmyyyydate{\today}.
\end{document}Output:

Change the separator of the numerical date
To change the separator of the numerical current date, you have to redefine the \dateseparator command with \renewcommand command. Like this.
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{<separator>}
In the you can use your preferred seperator. All of those are given below.
| Command | Output |
|---|---|
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{-} | 02-11-2023 |
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{--} | 02–11–2023 |
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{---} | 02—11—2023 |
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{.} | 02.11.2023 |
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{$\cdot$} | 02·11·2023 |
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{datetime}
\begin{document}
\renewcommand{\dateseparator}{---}
\textbf{Current date with em-dash separator:} \ddmmyyyydate{\today}.
\end{document}Output:
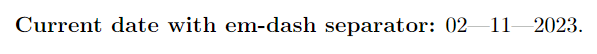
The datetime package provides more date format of the current. You can pass the <format> as an optional argument with the package like this.
usepackage[<format>]{datetime}
Follow the given table.
| Command | Output |
|---|---|
\usepackage[yyyymmdd]{datetime} | 02/11/2023 |
\usepackage[dmyyyy]{datetime} | 02/11/23 |
\usepackage[ddmmyy]{datetime} | 02—11—2023 |
\usepackage[dmyy]{datetime} | 2/11/23 |
\usepackage[mmddyyyy]{datetime} | 11/02/2023 |
\usepackage[mdyyyy]{datetime} | 11/2/2023 |
\usepackage[mmddyy]{datetime} | 11/02/23 |
usepackage[mdyy]{datetime} | 11/2/23 |
\usepackage[long]{datetime} | Thursday 2nd November, 2023 |
\usepackage[short]{datetime} | Thu 2nd Nov, 2023 |
\usepackage[us]{datetime} | November 2, 2023 |
\usepackage[text]{datetime} | Thursday the Second of November, Two Thousand and Twenty-Three |
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage[text]{datetime}
\begin{document}
\textbf{Current date in text:} \today.
\end{document}Output:
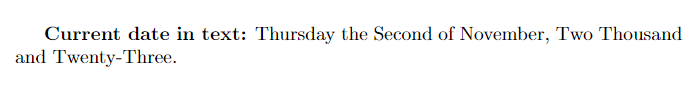
Also, you can use the <format> with the \today command but in this case you have to write an extra word with the <format>. You can get the same output either using \usepackage[yyyymmdd]{datetime} with \today command or \usepackage{datetime} with \mmddyyyydate{\today} command.
An advantage of this technique, you print more than one format of the current date at the same time.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{datetime}
\begin{document}
\textbf{Current date in ``month/day/year":} \mmddyyyydate{\today}.
\textbf{Current date in ``day/month/year":} \ddmmyydate{\today}.
\textbf{Current date in ``short":} \shortdate{\today}.
\textbf{Current date in ``us":} \usdate{\today}.
\end{document}Output:

Leave a Reply